systemd查看当前所有正在运行中的服务
systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running按启动时间排序查看所有进程
ps aux --sort=start_time查看当前谁在进行系统调用
需要安装 bpftrace ,安装好后执行:
bpftrace -e ' tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter_execve { printf("comm: %s, argv[0]:%s, argv[1]:%s, arg[2]: %s, arg[3]: %s, pid: %d, cpu: %d\n", comm, str(args->argv[0]),str(args->argv[1]), str(args->argv[2]), str(args->argv[3]), pid, cpu); }'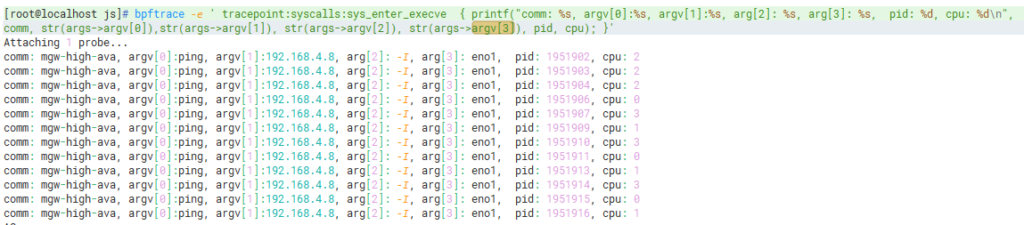
图中看到,mgw-high-ava 这个进程调用了ping 192.168.4.8 -I eno1 命令。
find怎么排除指定目录
排除一个目录用 -not -path “xxx” 或 ! -path “xxx” 。如果要想排除多个目录
find . -type f -name ".txt" -not -path "./example/*"
# 或者
find . -type f -name "*.txt" ! -path "./example/*" 如果要想排除多个目录,要用 -a 连结起来。
find . -type f -size +10M -not -path "./mirror/*" -a ! -path "*wp-data*"Bash中实现字符串大小写转换
使用Bash参数扩展方案,转大写:
echo "${str^^}"转小写:
echo "${str,,}"查看系统当中已被删除但未释放的文件
使用lsof命令,+L1,表示列出系统中所有 链接数小于1 的已打开文件,链接数为0表示文件已被删除(unlinked),但仍被某些进程占用(例如日志文件被删除但未释放)。
lsof +L1查看iptable是否是nftable兼容版本
使用iptables –version 命令。
[root@znl.pub ~]# iptables --version
iptables v1.8.4 (nf_tables)监控 Linux 下 /tmp 目录中创建 pymp-* 目录的进程
使用 auditd 审计系统。centos 8上面默认自带。
# 1. 查看auditd 服务是否已经运行 没有运行的话,我们启动它
systemctl status auditd
systemctl start auditd
# 2. 添加审计规则(监控/tmp下pymp-开头的目录创建)
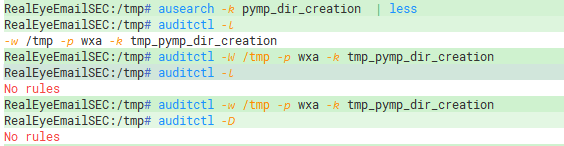
auditctl -w /tmp -p wxa -k tmp_pymp_dir_creation
# 3. 查看审计日志
ausearch -k pymp_dir_creation | less
# 4. 在less中,执行查找 pymp-
:/pymp-
# 以 ---- 为分割的一块区域为一个完整的审计事件,为了方便我们分析
# 5. 删除我们添加的auditd规则
# 首先列出规则
auditctl -l
# 找到要删除的规则,就拿我们上面使用的规则为例
-w /tmp -p wxa -k tmp_pymp_dir_creation
# 方法1:使用 -W 删除规则,将原规则复制粘贴并修改小w为大W。
# 针对文件/目录监视规则(-w 添加的),必须使用完全相同的参数删除
auditctl -W /tmp -p wxa -k tmp_pymp_dir_creation
# 方法2:清空所有规则,参数为 -D
auditctl -D 
查看启用的yum源都有哪些
yum repolist enabled Nginx 配置 HTTP Basic Authentication(401认证)
# 使用 htpasswd ,如果没有,centos需要执行本命令进行安装
yum install -y httpd-tools
# ubuntu 需要:
apt-get install apache2-utils
# 首次添加用户(-c 参数创建文件)
sudo htpasswd -c /etc/nginx/.htpasswd username1
# 后续添加用户(去掉 -c 避免覆盖)
sudo htpasswd /etc/nginx/.htpasswd username2
# 编辑 Nginx 配置文件,在 server 块中添加认证指令:
server {
listen 80;
server_name your_domain.com;
# 启用 Basic Auth
auth_basic "Restricted Access";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
location / {
...
}
}
Nginx 配置401认证后,排除特定路径(如公开api)
server {
listen 80;
server_name your_domain.com;
# 启用 Basic Auth
auth_basic "Restricted Access";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
location / {
...
}
location /public/ {
auth_basic off;
}
}
Nginx 配置401认证后,允许特定 IP 跳过认证
server {
listen 80;
server_name your_domain.com;
# 全局默认开启认证(但会被 location 覆盖)
auth_basic "Restricted";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
# 公共路径(完全开放)
location /public/ {
auth_basic off;
allow all; # 确保不继承外部的 deny all
}
# 受保护路径(IP白名单或认证二选一)
location / {
satisfy any;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
deny all;
# 其他配置(如反向代理、静态文件等)
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
}
}
带单位的数据大小求和运算
# 思路: 将M/G/T/P等单位转换成字节 ,再进行加运算,再转换成带单位的数值
# 假设数据是这样的(1.txt):
# "866.22KB"
# "3.41M"
# "3.52M"
cat 1.txt | sed 's/[kK][bB]/K/' | tr -d '"' |numfmt --from=si | paste -sd + | bc | numfmt --to=si批量删除目录中特殊字符文件
# 在 Linux 中,当文件名包含特殊字符(如回车符 \r、换行符、空格等)时,通过管道将 ls 的结果传递给 grep 或 while read 会导致解析错误
# 更好的方法是使用 find -print0 + while IFS= read -d '' + $(printf "%q" "$file") 处理任意文件名(包括特殊字符)
# 删除当前目录下所有文件(包括带特殊字符的文件)
find . -maxdepth 1 -type f -print0 | while IFS= read -r -d '' file; do
rm -- $(printf "%q" "$file")
done
# 删除当前目录下除特定文件名外的所有文件(包括带特殊字符的文件)
find . -maxdepth 1 -type f -print0 | while IFS= read -r -d '' file; do if ! [[ "$file" =~ (home|root|run|sbin|bin|boot|data|dev|etc|lib|lib64|media|mnt|opt|proc|srv|sys|tmp|usr|var|auto) ]] ; then echo rm -- $(printf '%q' "$file"); fi done | bash 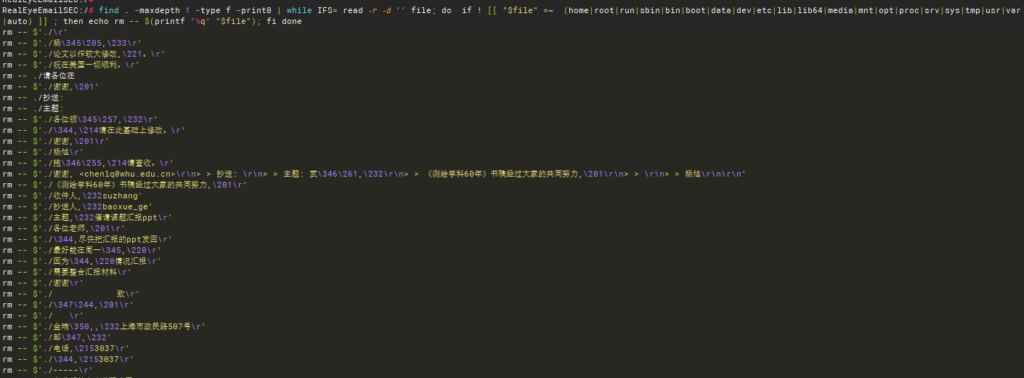
定时任务防止任务重叠,保证单例执行
# crontab 定时任务,有非常简单的方法实现单例执行,使用文件锁
*/5 * * * * root flock -n /tmp/control_logs.lock /scripts/run.sh stat >> /var/log/run.log 2>&1
删除某个文件夹下重复的文件(通过MD5比对进行文件去重)
declare -A seen; for file in *; do [[ -f "$file" ]] && md5=$(md5sum "$file" | awk '{print $1}') && [[ -n "${seen[$md5]}" ]] && rm -- "$file" || seen[$md5]=1; done
查看某个进程的父进程及完整的命令(树状查看)
pstree -asp PIDVMware虚拟磁盘空间缩小解决方案(linux 系统)
znl.pub:/# vmware-toolbox-cmd disk list
/
/data
/boot
/data/db
/boot/efi
znl.pub:/# vmware-toolbox-cmd disk shrink /
znl.pub:/# vmware-toolbox-cmd disk shrink /data
znl.pub:/# vmware-toolbox-cmd disk shrink /data/db
znl.pub:/# vmware-toolbox-cmd disk shrink /boot/efi
# 解释 vmware-toolbox-cmd disk shrink 命令会自动执行类似用 zero 填充剩余磁盘空间的功能(然后删除),然后通知外部虚拟机对(所有)挂载磁盘进行压缩。此时他也会暂停虚拟机,虚拟机是无响应的。每执行一次shrink命令都会触发一次所有磁盘压缩操作。